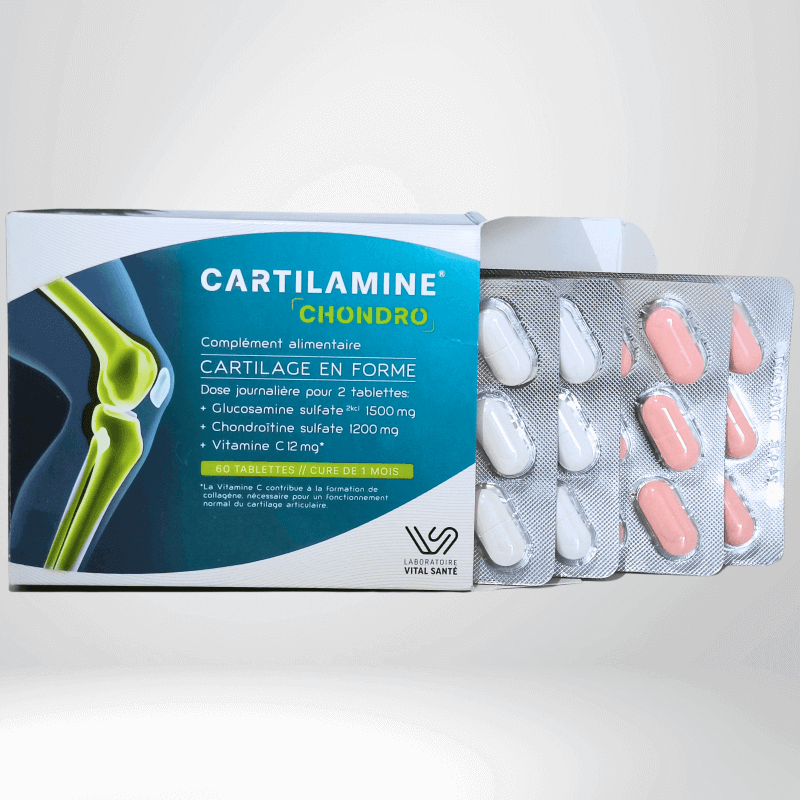
The influence of diet on joint pain
Partager
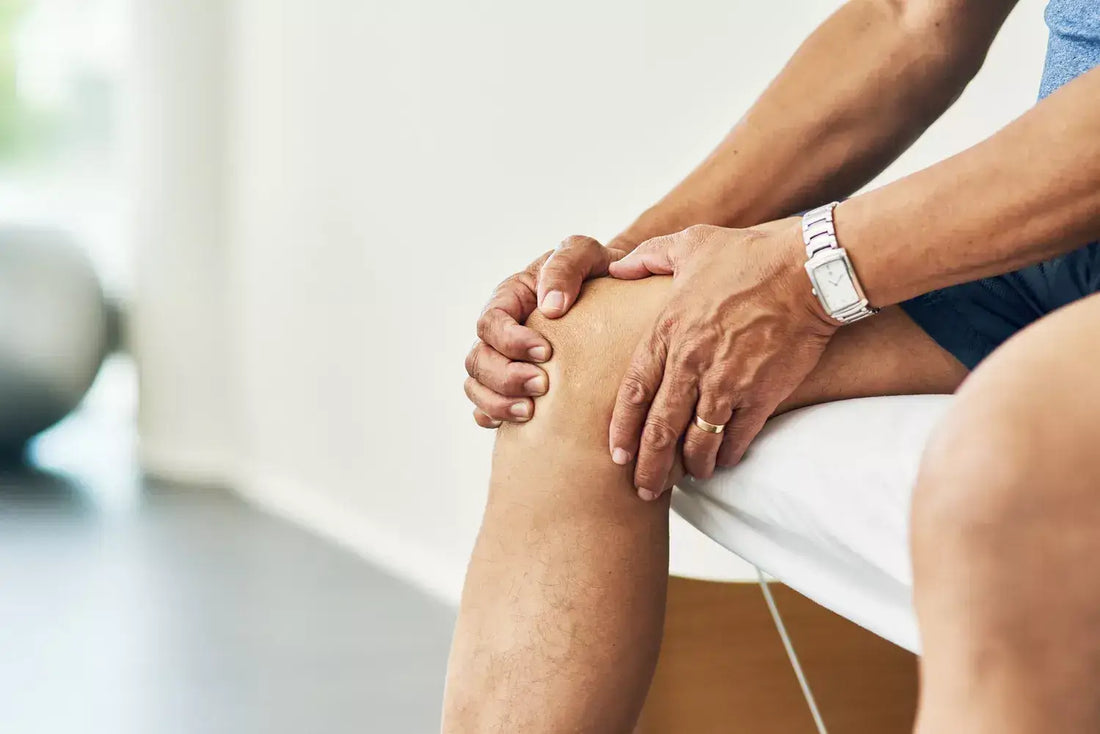
Joint pain can often be associated with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other forms of rheumatism. These conditions can cause significant discomfort in daily life and limit mobility. While various medical treatments are available to relieve this pain, it is important to recognize the importance of diet in managing joint symptoms.
Diet and inflammation
An unbalanced diet can contribute to inflammation in the body, which can make joint pain worse. Certain foods can trigger an inflammatory response, while others can help reduce inflammation. Foods high in added sugars, saturated fats, and chemicals can promote inflammation, while foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential nutrients can have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Foods to favor
Fresh fruits and vegetables, rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, are valuable allies in the fight against inflammation. Berries, citrus fruits, dark leafy greens, and colorful vegetables are especially beneficial. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in oily fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, have well-documented anti-inflammatory properties.
Avoid pro-inflammatory foods
Certain foods are known to promote inflammation and can make joint pain worse. It is recommended to limit processed foods, fatty meats, high-fat dairy products, added sugars, refined grains, and vegetable oils rich in omega-6 (such as corn oil and sunflower oil).
Maintain a healthy weight
Being overweight and obese puts extra strain on joints, especially the knees, hips, and spine. Losing weight can reduce the strain on joints and thus alleviate joint pain. Eating a balanced diet and getting regular physical activity are important strategies for maintaining a healthy weight.

Adequate hydration
Proper hydration is essential to maintain joint health. Water helps lubricate joints and keep them flexible. It is recommended to drink enough water throughout the day and limit sugary drinks and caffeine, which can have a dehydrating effect.
Ultimately, diet plays a crucial role in managing joint pain. By prioritizing a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, limiting pro-inflammatory foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying adequately hydrated, it is possible to reduce inflammation in the body and alleviate joint symptoms. Consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized advice on the best diet to support your joint health.