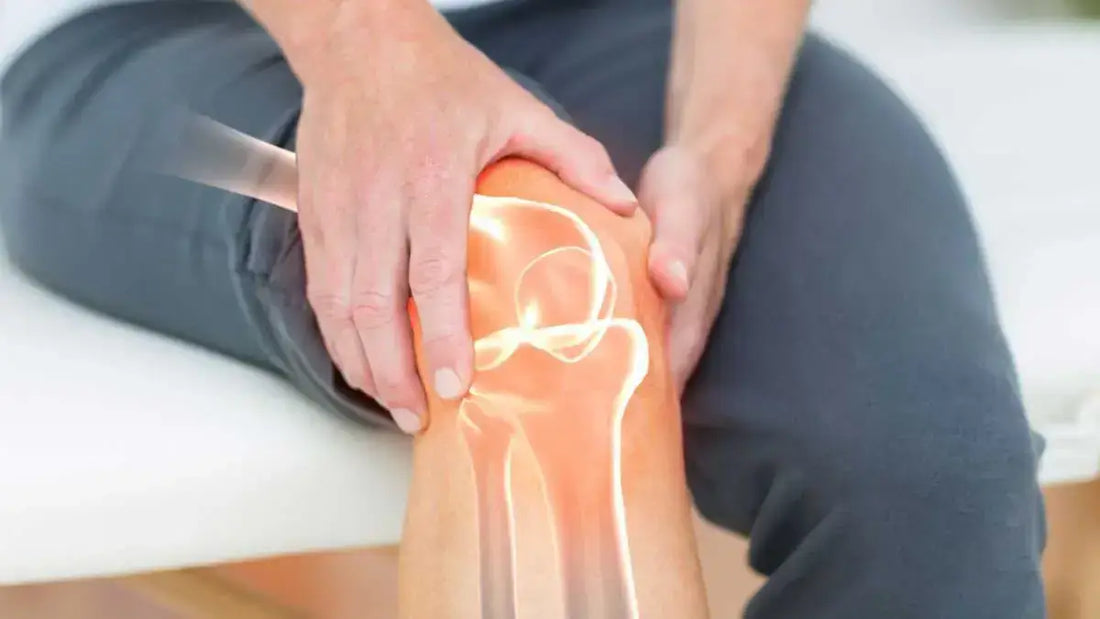
Gonarthrosis or knee osteoarthritis
Partager
The word gonarthrosis comes from two Greek words, “gono” meaning joint and “arthron” meaning inflammation.
Gonarthrosis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the joint between the femur and the kneecap (patellofemoral osteoarthritis), or between the femur and the tibia (tibial femorofemoral osteoarthritis).
Knee osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) is a chronic disease that damages the cartilage and bone of the knee.
It can be difficult to tell if you have knee osteoarthritis. Symptoms aren't always easy to notice, and it can take months or years for them to develop.
The pain associated with knee osteoarthritis may be intermittent and not always present at all times. It may be worse in cold weather or when the joint is bearing weight, but it may also just come and go for no apparent reason.
CAUSES OF GONATHROTHRASIS
Several factors can be responsible for knee osteoarthritis: poor posture, misalignment of the legs, and/or excessive stress on the joint (carrying heavy loads, being overweight).
A sedentary lifestyle can also play a significant role, but gonarthrosis can also be caused by trauma, such as a fall or injury.
Risk factors
Among all the risk factors, the one that mainly comes up in the most common cases of gonarthrosis, as you might expect, is being overweight, but we can also mention:
• Age: Obviously, joints become fragile over time and therefore age becomes a risk factor for the onset of chondropathy.
• Gender: there is an increase (after menopause) in knee osteoarthritis in women
• Diabetes is also a rapidly growing risk factor.
• Architectural anomalies: Genu varum or genu valgum
• Heredity
• The different joint traumas
• Certain professions: whose activity requires a lot of leg flexion, such as tilers for example who are constantly on the ground.
• Intensive sports practice: football, skiing, rugby, etc.
SYMPTOMS OF GONATHROTHRASIS
The symptoms of knee osteoarthritis are mainly:
• swelling
• pain
• stiffness
• a limitation of movements.
Osteoarthritis between the femur and the tibia (femoro-tibial): manifests itself by “mechanical” pain in the knee which results in a limitation of knee mobility.
Knee pain is more noticeable when you go up or down stairs, or while walking. It is usually not painful when your joint is at rest.
Osteoarthritis between the femur and the kneecap (patellofemoral): manifests itself by knee pain when going down stairs and when sitting for a long time. The pain intensifies when bending the knee, a cracking or crepitating sensation when bending the knee is usually noted.
The progression is often random: the pain is intermittent at first, then bothersome, particularly when playing sports.
TREATMENTS FOR GONATHROTHRASIS
Knee osteoarthritis can be difficult to treat, but there are several treatment options that can help relieve pain and improve joint mobility. It's important to talk to a doctor to find the best treatment for your situation.
Here are some treatment options for knee osteoarthritis:
• Nutritional coaching (in case of overweight)
• Wearing a knee brace
• Apply heat or cold to your kneecap (hot for stiffness and cold for pain)
• Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility and mobility of the joint.
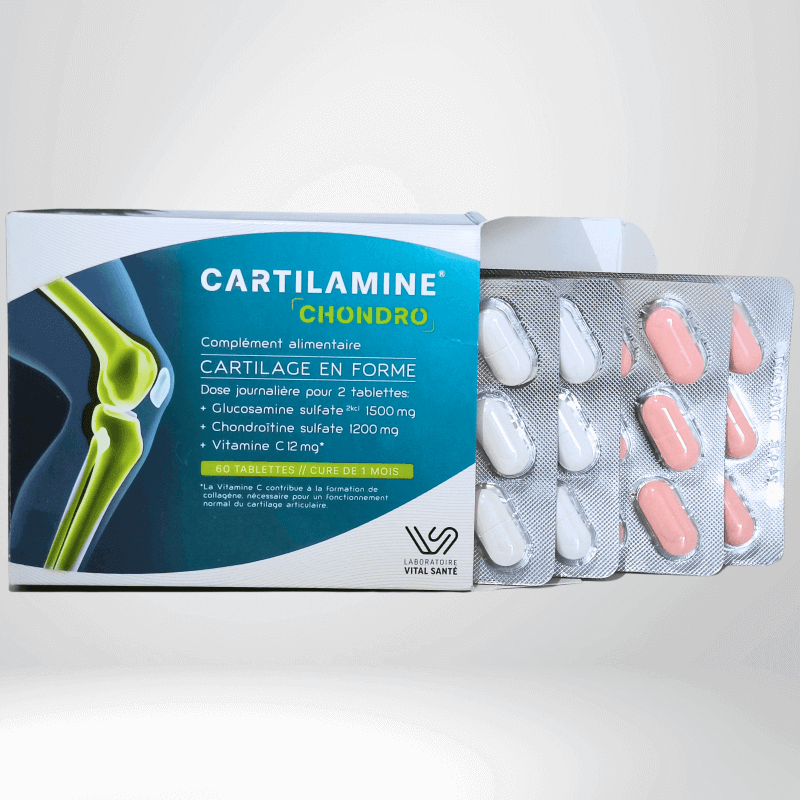
• Slow-acting symptomatic anti-arthritics for several months.
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain and inflammation but beware of side effects.
• Corticosteroid injections may also be used to relieve pain.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to replace the damaged joint surface with synthetic bone or a knee replacement.

GONATHROTHROSIS AND SPORT
It is important to stay active when you have knee osteoarthritis, but it is also important to choose activities that do not put too much stress on your knees. For example, you can try water activities such as swimming or water aerobics, as the water supports your weight and reduces the pressure on your knees. You can also try activities such as cycling or walking, being careful not to put too much strain on your knees. Flexibility exercises are also recommended.
It is important to remember that everyone is different and exercises that work for one person may not be appropriate for another. Talk to your doctor, physical therapist for advice on activities that are right for your health and needs.





3 comments
J’ai très mal aux genoux pourriez vouzs m’aider à guérir cette maladie svp
Bonjour
J’ai le devant du genou droit qui est
Légèrement tiède et enflé….j’ai mal
Lorsque je descend des marches….
Merci beaucoup de vos solutions
merci de vos conseils, mes genoux se portent bien.
Par contre: puis-je vous commander en direct des comprimées de COGNITO, pour la mémoire ? J’ai testé une boîte , cela était très efficace, et n’en ai plus retrouvé depuis…
Merci d’avance. D’autre part je prends VEINAVITAL depuis 1 an et en suis très satisfaite.
Recevez mes meilleures salutations.